Layer Boolean Operations
KLayout now comes with a set of boolean operations. These operations are available in the "Layers" submenu of the "Edit" menu ("Boolean Operations" and "Merge" functions). A dialog will open that allows specification of mode, input layer(s), output layer and certain other options.
- AND: intersection. The output layer will contain all areas where shapes from layer A and layer B overlap.
- A NOT B: difference. The output layer will contain all areas where shapes from layer A are not overlapping with shapes from layer B.
- B NOT A: difference. The output layer will contain all areas where shapes from layer B are not overlapping with shapes from layer A.
- XOR: symmetric difference. The output layer will contain all areas where shapes from layer A are not overlapping with shapes from layer B and vice versa.
In addition, a MERGE operation is provided, which is a single-layer operation that joins (merges) all shapes on the layer. As a special feature, this operation allows selecting a minimum overlap count: 0 means that output is produced when at least one shape is present. 1 means that two shapes have to overlap to produce an output and so on. This does not apply for single polygons: self-overlaps of polygons are not detected in this mode.
All operations can be performed in three hierarchical modes:
- Flat: Both layers are flattened and the results are put into the current top cell.
- Top cell: perform the operation on shapes in the top cell only.
- Cellwise: perform the operation on shapes of all cells below the current top cell individually. This mode is allowed only if the layouts of both inputs and output are the same.
For the first two modes, the source and target layout can be different, provided that all layouts are loaded into the same view. This allows combining layers of different layouts. For example to compare them using a XOR function.
As a special feature, KLayout's boolean implementation allows choosing how "kissing corner" situations are resolved. KLayout allows two modes:
- Maximum coherence: the output will contain as few, coherent polygons as possible. These polygons may contain points multiple times, since the contour may return to the same point without closing the contour.
- Minimum coherence: the output will contain as much, potentially touching polygons as possible.
The following screenshots illustrate the maximum coherence (left) and minimum coherence (right) modes for a XOR operation between two rectangles.
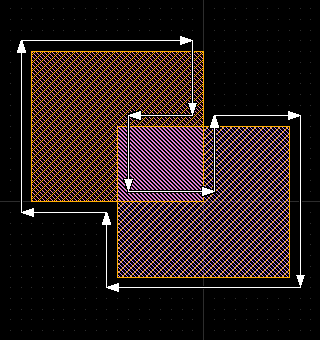
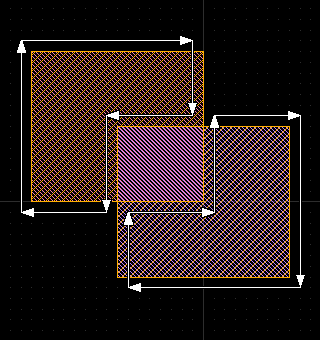
The boolean operations are currently implemented flat and based on a full-level edge representation. This means, that the complete layer is flattened (if "flat" mode is requested) and converted into a set of edges which the processor runs on. This will lead to huge resource requirements for very large layouts and is not recommended for such applications currently.
The boolean processor is based on an iterative approach to cover grid snap effects which makes it highly accurate but somewhat slower than a single-pass scanline implementation. Performance penalty is about 2x (two times slower) compared to an efficiently implemented single-pass algorithm.